Temperature-Dependent Current–Voltage Characterization of Solar Cells
During this practical, you will investigate how temperature influences the electrical performance of a silicon solar cell by measuring its current density–voltage (J–V) characteristics under different temperature conditions.
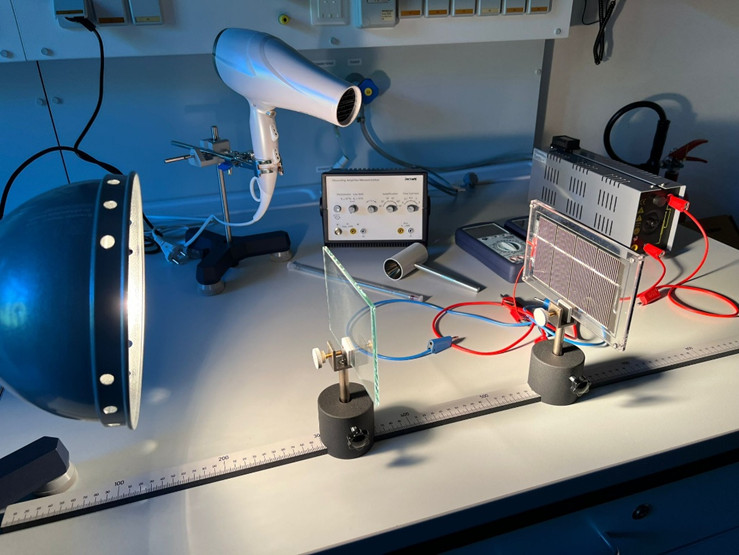
Figure 1. The experimental setup for temperature-dependent J-V characterization
As shown in Figure 1, you will use a heater to have temperature-control and a solar simulator to perform systematic J–V measurements over a defined temperature range. The aim is to analyze the temperature dependence of key photovoltaic parameters (open-circuit voltage (Voc), short-circuit current (Jsc), fill factor (FF), efficiency) and to understand underlying loss mechanisms such as recombination pathways and series resistance effects.
You Will ...
- Calibrate the illumination intensity at room temperature to approximate standard test conditions.
- Measure baseline J–V curves of the silicon solar cell at room temperature in both dark and illuminated conditions.
- Vary temperature stepwise, allowing thermal equilibrium at each point
- Record J–V curves at each temperature and extract key solar cell parameters
- Plot results to show the dependence of Voc, Isc, and efficiency on temperature.
- Analyze trends to observe how Voc and Jsc typically changes and evaluate the combined impact on efficiency
Detailed experimental Work
- Verify solar simulator intensity at room temperature. Calibrate temperature and confirm stable control over the entire measurement range.
- Perform J–V measurements at multiple temperatures.
- Measure dark current.
Data Analysis: Plot Voc vs. T and Jsc vs T. Fit to extract bandgap and recombination activation energy. Analyze series resistance and shunt resistance temperature trends.
You Will Learn ...
• How temperature affects solar cell parameters and efficiency.
• The relationship between Voc and intrinsic material properties such as bandgap.
• How to distinguish recombination-limited vs. resistive losses from temperature-dependent data.
• Best practices for thermal control and avoiding measurement artifacts.